Innovating Bridge Inspections with BIM and GAMMA AR for Safer Infrastructure Management

Table of Contents
Share this post
Problem: Traditional bridge inspection often results in inconsistent and scattered data, complicationg efforts to maintain thorough records and ensure infrastructure safety.
Impacts: These challenges affect Brazil’s 137,000+ bridges as well as bridges worldwide, where documentation gaps can lead to maintenance delays, safety risks, and higher long-term costs.
Solution: Researchers at the Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV) developed a workflow using BIM with GAMMA AR to enhance real-time data collection and precise, onsite documentation.
Results: The new methodology optimizes inspections, improves data accuracy, and offers a centralized model for bridge maintenance with the potential to boost safety and efficiency on a global scale.
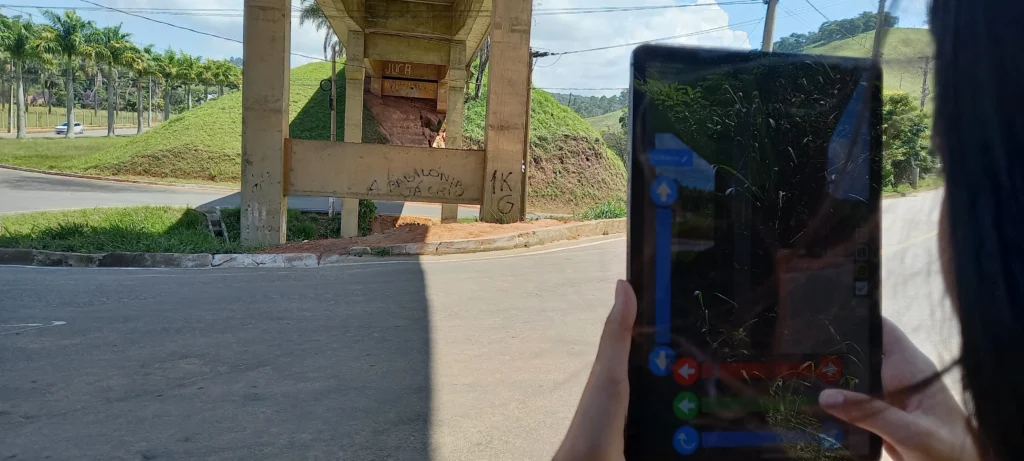

Bridge inspections are critical for infrastructure safety and longevity.
Unfortunately, traditional methods often fall short in data consistency, making it difficult to compile and maintain thorough records.
In Brazil, with over 137,000 bridges, this problematic issue underscores the need for new methodologies.
Recognizing this, researchers at the Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV) developed an innovative workflow integrating Mixed Reality (MR) and Building Information Modeling (BIM).
Their objective was to improve documentation precision and streamline visual inspections, creating a more comprehensive record of bridge conditions over time.
The team, led by Dr. Ana Carolina Pereira Martins with co-researchers including Isabele Rocha Castellano and others, partnered with Brazil’s National Department of Transportation Infrastructure (DNIT) to test their methodology.
They focused on the Coimbra I Viaduct, chosen for its proximity to UFV.
The study’s goal was to validate a data-rich, tech-forward approach that could improve inspection documentation and bridge pathology tracking over the structure’s lifecycle.
Streamlining Bridge Documentation with BIM and Mixed Reality
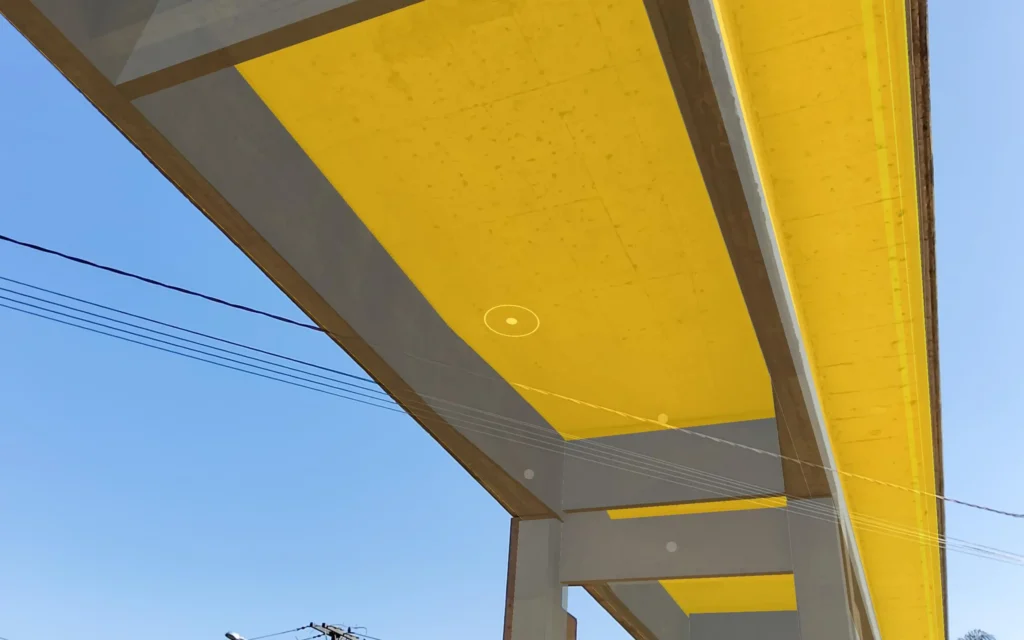

Standard visual inspection methods can lead to inconsistent data across various media formats, complicating bridge maintenance records.
The UFV team’s approach combines BIM and MR to address these documentation issues.
BIM serves as a dynamic digital model of the structure, capturing the bridge’s geometry and condition history, while MR overlays digital information onto physical structures to support real-time documentation.
This workflow enables inspectors to interact with a data-rich, 3D representation of the bridge, capturing structural details directly on-site.
“Currently, bridge inspections often rely on forms, reports, and photos, which scatter data across different formats and media, leading to delays and inaccuracies,” said Dr. Martins. “By integrating Mixed Reality through GAMMA AR, we aimed to optimize the process, making it not only faster and safer but also more precise in capturing and documenting damage.”
Methodological Steps and Technological Integration
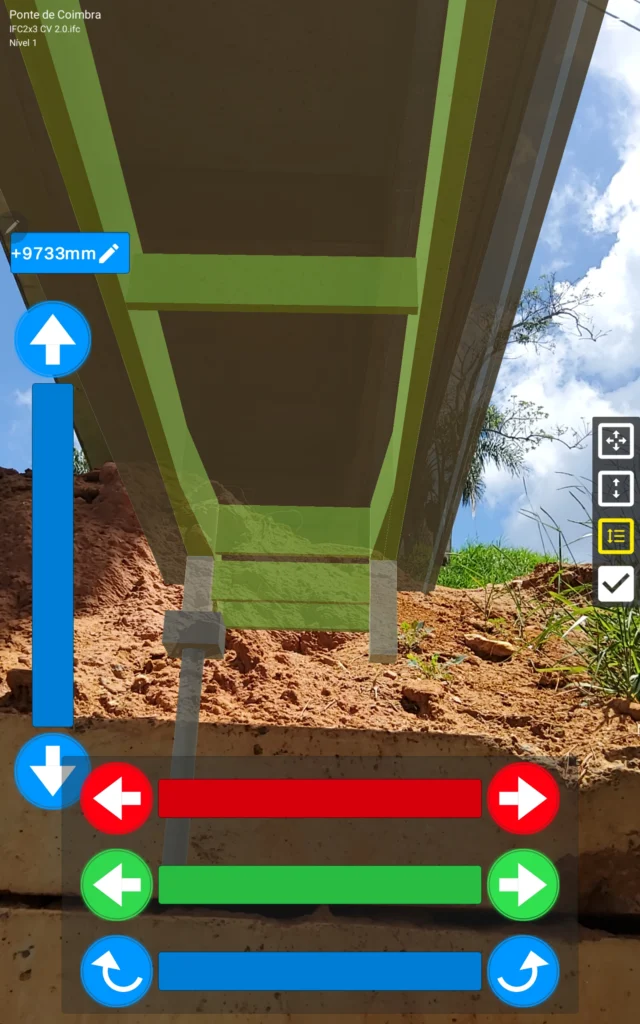
The inspection of the Coimbra I Viaduct validated the new methodology, building on prior research with point cloud modeling.
The initial point cloud, which provides a high-resolution digital model, was created during a previous study and used as the foundation for further BIM integration.
- Creation of the BIM Model: Using Autodesk Revit, the team created a BIM model, integrating geometric data from UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) surveys. This digital model allowed inspectors to systematically document bridge details and pathologies for long-term tracking.
- Integration with GAMMA AR: The BIM model was then imported into GAMMA AR, an augmented reality solution that overlays digital models onto physical structures via tablets or smartphones, facilitating on-site data collection. Dr. Castellano said, “After testing various tools, GAMMA AR stood out for its ability to properly integrate with our BIM workflow. Its use of open-standard file formats like IFC and BCF made it ideal for the level of interoperability we needed. It was the perfect fit for advancing our research objectives.”
- First On-Site Inspection and Model Alignment: During the initial inspection, the team used GAMMA AR to align the BIM model with the viaduct by setting reference points, such as Pillar P8. This alignment enabled inspectors to document structural observations, including minor cracks and concrete spalling (surface damage and deterioration), directly onto the digital model. “GAMMA AR helped us solve a significant challenge of inspecting hard-to-reach areas by allowing us to visualize and document damage remotely and safely,” Dr. Castellano explained.
- Damage Analysis and Documentation: With the first round of data collected, the team returned to the office to review and integrate findings into the BIM model using Revit and the BCF Manager plugin. The captured data, organized in parametric families, now serves as a digital repository for the bridge’s condition history. Dr. Martins noted, “The widespread adoption of AR in infrastructure could significantly improve public safety by enabling more frequent and thorough inspections. It reduces the risk to workers, speeds up maintenance decisions, and ensures that damage can be detected early, before it poses a threat to public safety.”
- Second Inspection and Data Validation: The follow-up inspection used GAMMA AR to confirm previously recorded damage data, utilizing the app’s measurement tool to assess the extent of minor structural issues and verify the locations of pathologies within the BIM model. This final step validated the accuracy of the documented data and reinforced the utility of the integrated MR-BIM methodology for future maintenance planning.
Outcomes and Potential for Widespread Application
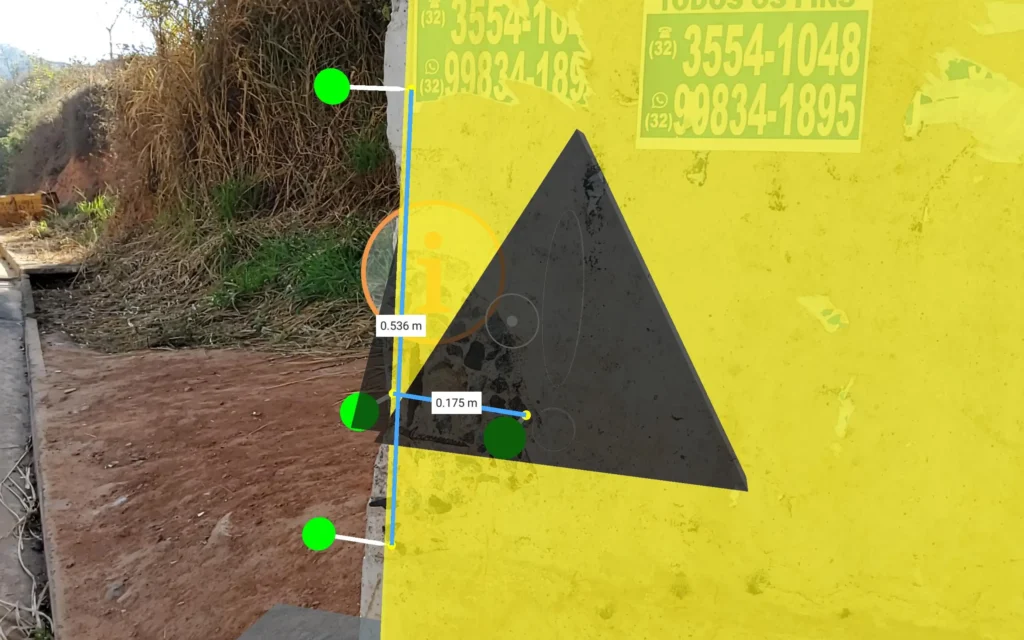

By centralizing documentation in a BIM model enhanced with MR, the workflow improved data access and resolved inconsistencies common to traditional methods.
The new workflow minimized manual data entry and supported extensive real-time data sharing, optimizing both accuracy and efficiency.
- Enhanced Documentation Accuracy: Augmented reality allowed inspectors to overlay damage directly onto the bridge’s BIM model, providing precise and consistent records for future reference.
- Increased Data Access and Efficiency: By using real-time synchronization with the office, the team streamlined workflows, reducing errors and improving access to up-to-date inspection records.
- Improved Safety: The ability to conduct inspections with tablets minimized the need for physical access to challenging or elevated areas, reducing risks for inspectors without sacrificing coverage.
Future of BIM and MR in Infrastructure Management
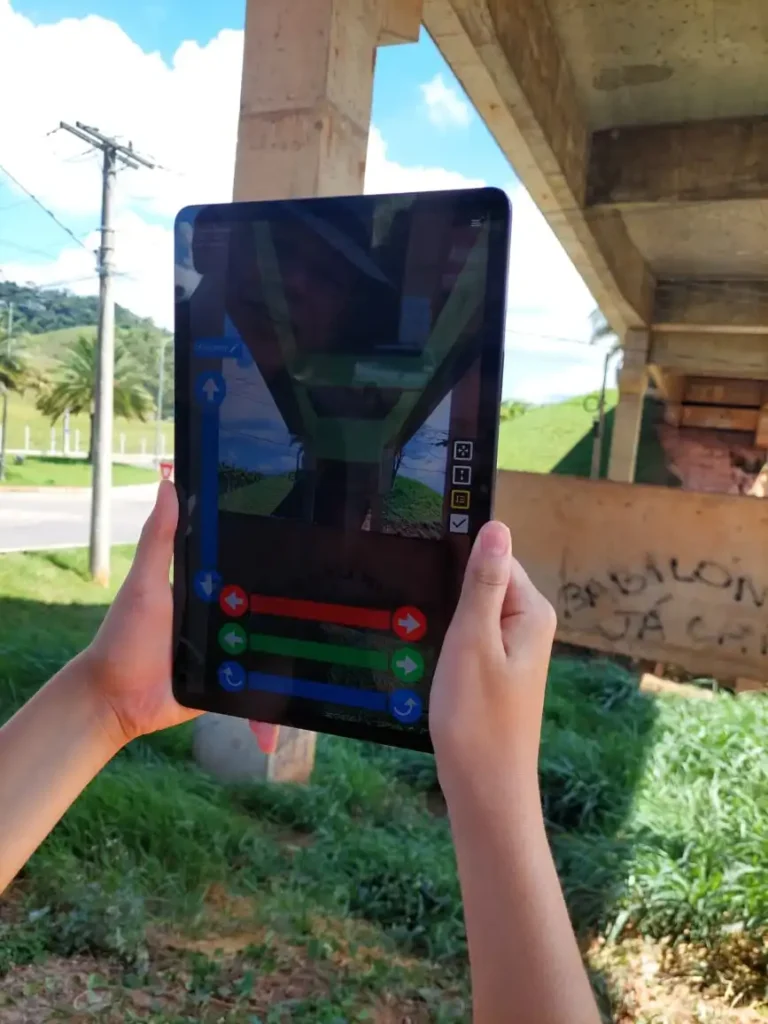

This study demonstrates that combining BIM and AR via tools such as GAMMA AR offers a promising approach for bridge inspections, particularly for documenting structural pathologies over a bridge’s lifecycle.
The success of this project points to broader applications within Brazil and beyond, with potential integration into Bridge Management Systems (BMS) for a consistent and centralized approach to infrastructure maintenance.
Supported by DNIT and published in the journal Automation in Construction (DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105775), the Coimbra I Viaduct project exemplifies a scalable model for tech-forward infrastructure management.
Advances in MR-compatible devices like LiDAR-enabled tablets could make BIM and MR methodologies a global standard, offering safer, more reliable, and cost-effective infrastructure management.
Ready to see how GAMMA AR can make all the difference in your inspection or construction projects?
Download a free trial from the App Store or Google Play and experience the benefits of augmented reality for safer, more efficient site management.
¹ Source for Images 1–4: Martins, A.C.P., Castellano, I.R., César Júnior, K.M.L., Franco de Carvalho, J.M., Bellon, F.G., de Oliveira, D.S., & Ribeiro, J.C.L. (2024). “BIM-based mixed reality application for bridge inspection.” Automation in Construction, Volume 168, Part A, 105775. Elsevier.
